Rooting enables all the user-installed applications to run privileged commands that are typically unavailable to the devices in their stock configuration. Rooting is required for more advanced and potentially dangerous operations including modifying or deleting system files, removing carrier- or manufacturer-installed applications, and low-level access to the hardware itself (rebooting, controlling status lights, or recalibrating touch inputs.) A typical rooting installation also installs the Superuser application, which supervises applications that are granted root or superuser rights. Via [
Wikipedia]
Android is less restrictive than few platforms. Google actually allows apps that require root access on the Google Play app store. There are quite a few attractive choices available that only run with elevated privileges. Let’s approach some of the major advantages to rooting Android.
1. Increase performance: If you want to have a good speed smartphone or tablet that runs the popular open-source operating system then overclocking is the way to go. There are many apps already available on Google Play that allow users to overclock the processor.
2. Protects the device: Smartphones and tablets are expensive and for some people that keeps valuable and private information. It’s natural to want to keep them safe.
Avast! Mobile Security and
Cerberus anti theft are two apps currently available on Google Play that work best with rooted device.
3. Remove bloatware: If you like to remove unnecessary apps from your device, Carriers for instance include branded software that is often unremovable, which is where having elevated privileges comes in handy. (Bloatware): Software whose usefulness is reduced because of the excessive disk-space and memory it requires.
5. Configure Restricted Settings: Do you want to enable fast charge in order to speed up the process of charging the device via USB? It can do that too. File managers such as Total Commander when paired with elevated privileges allow users to have access to various system files, allowing to modify the hosts file.
See Also >> Free Mobile Recharge By Sending Free SMS In India
Now Steps to Root Android Smart Phone:
Step 2: Now Connect your Android Phone to Computer and make sure that the SD card is not mounted. Now enable USB debugging on your phone by going to Settings >Applications >Development and enabling USB Debugging (see below).
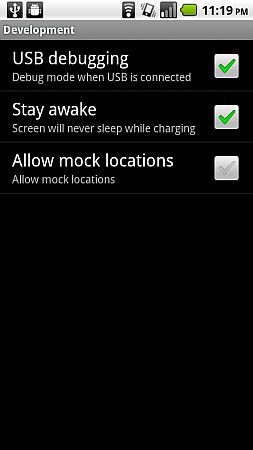
Enable USB Debugging
Step 3: Now go to that downloaded file and run SuperOneClick.exe.
Click Root to Root Your Phone
Step 5: Now wait, You may see warnings, but as long as it doesn’t hang on waiting for device, the process you can see on the screen should keep scrolling until it finally returns with the Success! message.
Step 6: Once finished, reboot the phone and you can see new SuperUser Icon in your installed apps. If you see it, then its confirmed your Android phone is rooted.
Note: Rooting is a guilty pleasure. The practice may start out innocently, but can void the phone’s warranty. Some manufacturers try to prevent users from running apps with elevated privileges.


